Understanding Advanced Authorization (AA) and Duty Free Import Authorization (DFIA)
In international trade, reducing production costs and enhancing competitiveness are crucial for exporters. The Indian government offers schemes like Advanced Authorization (AA) and Duty-Free Import Authorization (DFIA) to facilitate duty-free import of raw materials, components, or capital goods required for manufacturing export products. These schemes help exporters procure essential inputs without paying customs duties, thereby lowering costs and promoting export growth. While both schemes aim to boost exports, they differ in their eligibility, scope, and flexibility, making it important for exporters to choose the right scheme based on their sourcing and manufacturing needs.
Let us understand what is AA and DFIA
1. Advanced Authorization (AA) Scheme
Purpose:
-
To promote exports by allowing duty-free import of inputs (raw materials, components, consumables, capital goods) required to manufacture export goods.
Key Features:
-
Issued by DGFT (Directorate General of Foreign Trade) in India.
-
Allows import of inputs without paying customs duty.
-
Inputs imported under AA must be used for producing export goods.
-
Typically linked to physical exports (goods that will leave India).
-
Usually comes with export obligation: you must export goods of equivalent value within a specified period.
Example:
-
A garment manufacturer wants to import fabric and buttons to manufacture shirts for export. Using AA, they can import these duty-free, provided the shirts are exported.
2. Duty-Free Import Authorization (DFIA)
Purpose:
-
To allow duty-free import of inputs for export product manufacturing, primarily to save foreign exchange and reduce production cost.
Key Features:
-
Also issued by DGFT.
-
Inputs are imported without paying basic customs duty, and sometimes other duties like excise or VAT may apply.
-
DFIA can be issued for indigenous or imported inputs, but mostly focuses on raw materials/components that are not easily available domestically.
-
Export obligation is mandatory; you must export goods after using the imported materials.
-
Often considered a substitute of Advance Authorization, especially when local sourcing is allowed but import of some items is required.
Example:
-
A manufacturer of toys imports plastic granules duty-free to produce toys for export. DFIA ensures no customs duty on imported raw materials.
Now let us understand the difference between AA and DFIA. Also, let us know when to use which scheme
Which Should Be Used When?
-
Use Advanced Authorization (AA):
-
When importing raw materials, components, or capital goods that are not available in India.
-
When the export product is to be shipped abroad, and you want full duty exemption on imported inputs.
-
-
Use Duty-Free Import Authorization (DFIA):
-
When you want duty-free import of raw materials, especially if some local sourcing is possible.
-
Useful when exporting goods where part of the inputs is imported, and the rest may be domestic.
-
More flexible for mixed sourcing and reduces cost of production for exports.
-
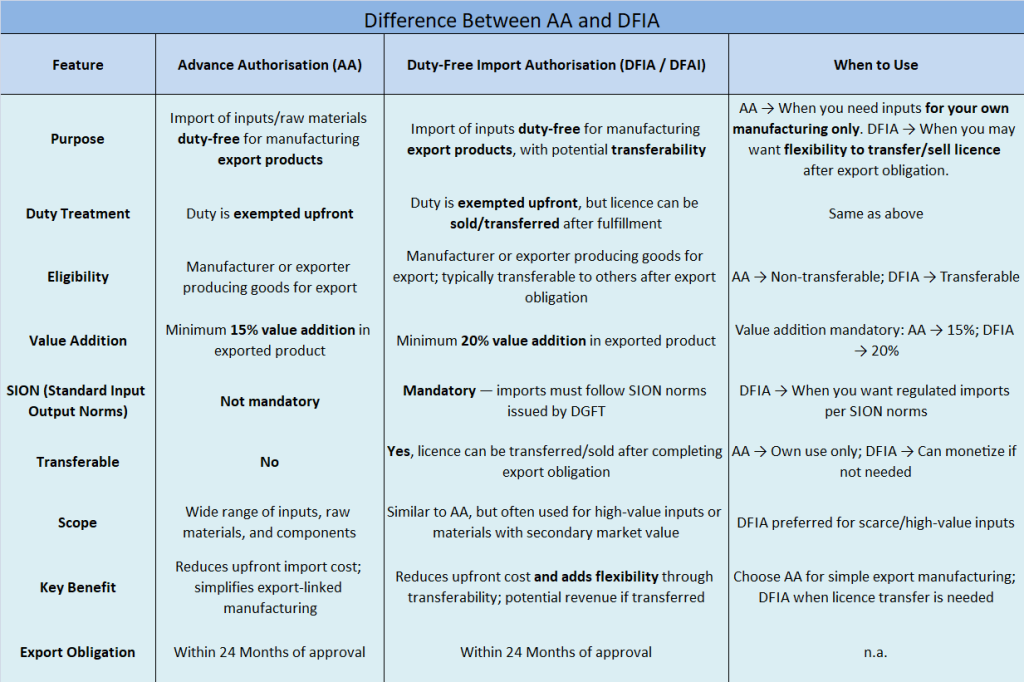
Summary
-
Both schemes aim to promote exports by reducing input costs.
-
AA is stricter, mainly for imported inputs not available domestically.
-
DFIA is more flexible, can include domestic sourcing, and is easier for manufacturers with mixed inputs.
