Packaging of Products
Packaging is the process of wrapping, covering, or containing a product in a way that protects it, makes it easy to handle, store, transport, and present to the customer.
It includes everything from the inner packing (like plastic wrap or pouches) to the outer packing (like cartons or pallets).
Packaging keeps your product safe, fresh, and attractive until it reaches the buyer.
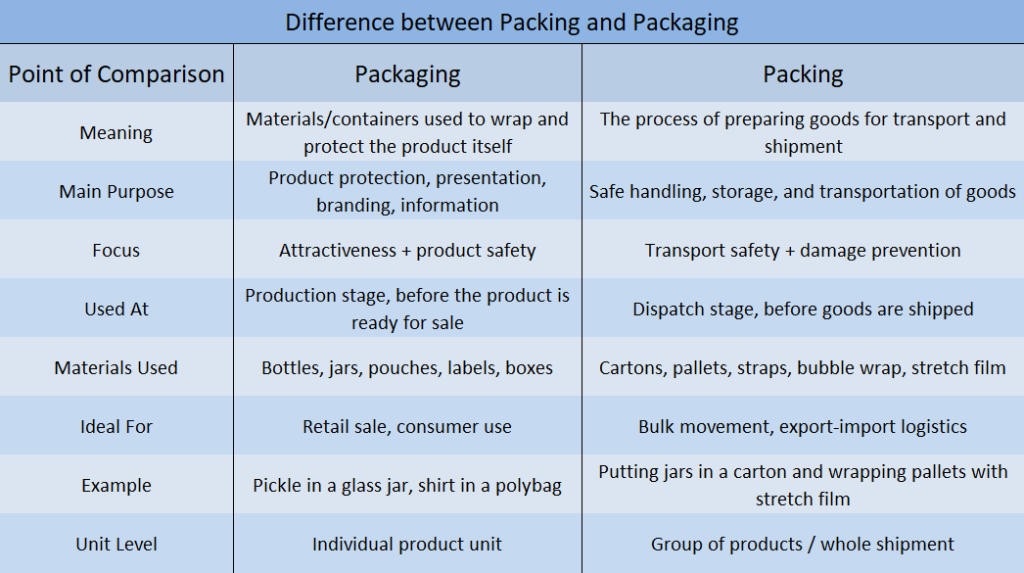
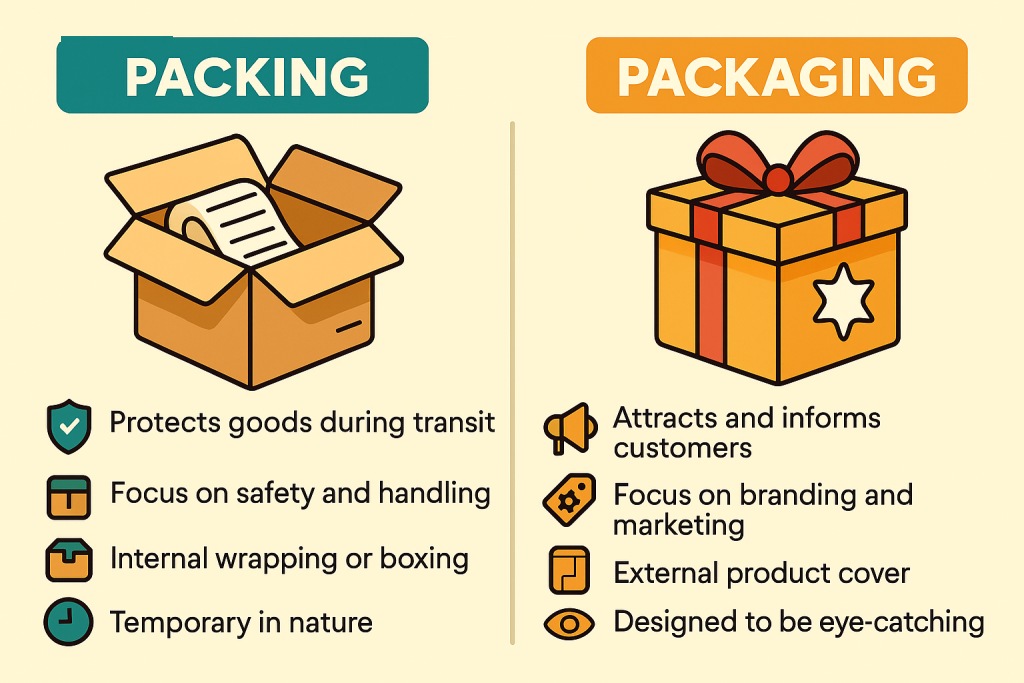
What is the Difference between Packing and Packaging
Importance of Packaging
- Protects the product from damage, moisture, dust, leakage
- Helps in easy transportation and storage
- Gives information like MRP, expiry date, ingredients
- Makes the product look attractive for selling
- Helps in branding & marketing
- Required for export compliance and safety
Understanding different layers of Packaging
Primary Packaging
- What it is: The first layer that directly touches the product.
- Purpose: Protects the product and provides information.
- Example: Bottle for juice, jar for pickle, polybag for shirt.
- Secondary Packaging
- What it is: The layer that groups primary packages together.
- Purpose: Makes handling, storage, and branding easier.
- Example: Cardboard box holding 12 jars of pickle, carton with 10 shirts.
- Tertiary / Transit Packaging
- What it is: The outermost packaging used for bulk transport.
- Purpose: Protects goods during shipping, stacking, and handling.
- Example: Palletized cartons wrapped with stretch film, wooden crates for machinery.
- Protective Packaging
- What it is: Extra material used to prevent damage.
- Purpose: Absorbs shocks, avoids scratches, protects from moisture.
- Example: Bubble wrap, foam sheets, thermocol, silica gel packets.
- Outer / Display Packaging
- What it is: Packaging designed to attract consumers in stores.
- Purpose: Enhances appeal, marketing, and brand recognition.
- Example: Printed boxes of chocolates, attractive sachets of spices.
- Specialized / Export Packaging
- What it is: Packaging made to meet transport, regulatory, or environmental needs.
- Purpose: Ensures safety, compliance, and durability during long-distance shipment.
- Example: Moisture-proof bags, vacuum-sealed food, temperature-controlled packaging, hazardous material packaging.


