What are Lab-Grown Diamonds?
Lab-grown diamonds (also called synthetic diamonds or man-made diamonds) are real diamonds created in a laboratory under controlled conditions that mimic the natural process by which diamonds form in the Earth’s crust.
They have the same physical, chemical, and optical properties as natural diamonds — both are pure carbon crystals arranged in a cubic structure.
Key Points about Lab-Grown Diamonds (LGDs):
-
Composition: 100% pure carbon crystal, just like natural diamonds.
-
Methods of Creation:
-
HPHT (High Pressure High Temperature)
-
CVD (Chemical Vapor Deposition)
-
-
Properties: Chemically, physically, and optically identical to mined diamonds (hardness, brilliance, sparkle are the same).
-
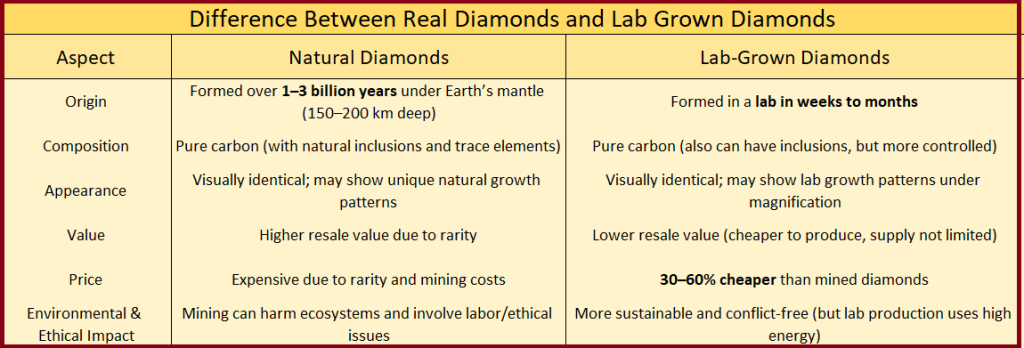
Difference from Natural Diamonds: Only the origin — natural ones form over billions of years underground, while LGDs are made in a lab in weeks to months.
-
Cost: Generally 30–60% cheaper than natural diamonds.
-
Sustainability: Considered more ethical and eco-friendly as they avoid mining-related issues.
These LGDs are made in Laboratories. There are TWO methods of manufacturing lab Grown Diamonds:
There are two main methods:
-
HPHT (High Pressure High Temperature): Replicates the intense pressure and heat deep inside the Earth.
-
CVD (Chemical Vapor Deposition): Uses carbon-rich gases in a vacuum chamber to slowly build diamond layer by layer.
-
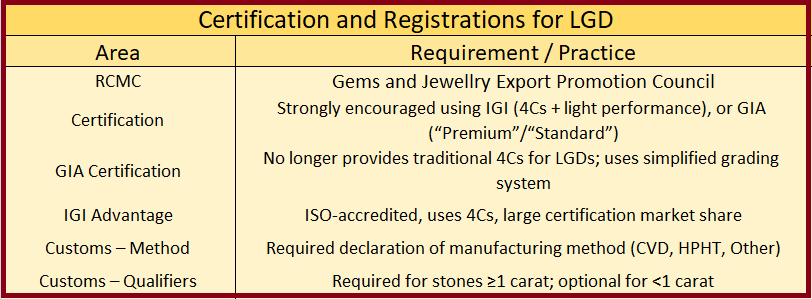
HS Code: 71049010 (Synthetic/Reconstructed Diamonds).
-
CBIC Circular Compliance:
-
≥1 carat stones → Mandatory: method + additional qualifiers (cut, clarity).
-
<1 carat stones → Method declaration mandatory, qualifiers optional.
-
Difference between Lab-grown and Natural Diamonds
Main Sourcing Hubs of Lab grown Diamonds
- Mumbai
- Surat
By far, China is the leading manufacturing hub for Lab-grown diamonds in the world. India is slowly catching up.
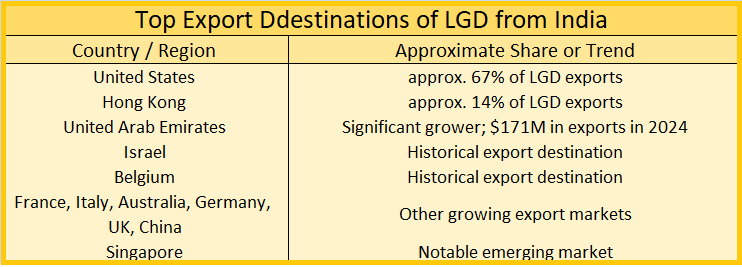
Top Exporting countries of Lab-grown diamonds are:
- China: As the world’s largest producer of lab-grown diamonds by volume, China is also a major exporter, supplying both industrial and gem-quality diamonds to the global market.
- India: A dominant force in the global diamond trade, India leads in lab-grown diamond exports, particularly after cutting and polishing. Surat is a major hub for this industry.
- United States: The U.S. is both a large consumer and a significant re-exporter of lab-grown diamonds. It is home to many trading companies and jewelers who are part of the global supply chain.
- Hong Kong: Acting as a crucial gateway to the Chinese market, Hong Kong is a major re-export center for both natural and lab-grown diamonds.
- United Arab Emirates: With Dubai emerging as a global trading center, the UAE has grown significantly as an exporter of diamonds, including lab-grown varieties.
Certificates and Registrations
Quality Parameters for LGDs (Export Standards)
1. The 4Cs – Traditional Diamond Standards
Even for LGDs, the 4Cs remain the universal parameters:
-
Carat Weight – Size of the diamond, measured in carats (ct).
-
Cut – Quality of proportions, symmetry, and polish; affects brilliance and sparkle.
-
Color – Graded from D (colorless) to Z (light yellow/brown).
-
Clarity – Graded from IF (Internally Flawless) to I3 (Included).
Exporters usually deal in higher grades (e.g., D–H color, VVS–VS clarity, Excellent–Very Good cut) as these are most in demand internationally.
2. Growth Method Identification
-
HPHT (High Pressure High Temperature) or CVD (Chemical Vapor Deposition) must be clearly declared in exports (mandatory under CBIC circulars from Dec 2024).
-
Certification labs (IGI, HRD, GIA) mention the growth method on reports.
3. Additional Technical Parameters
-
Fluorescence – Degree of glow under UV light (None, Faint, Medium, Strong).
-
Symmetry & Polish – Graded separately (Excellent, Very Good, Good, etc.).
-
Light Performance – Advanced grading of brilliance, fire, and contrast (especially by IGI).
-
Inclusions/Graining Patterns – Some buyers want assurance that LGDs are free from metallic inclusions (especially in HPHT).
4. Certification Parameters (Required by Buyers)
Export markets prefer third-party certification from leading labs:
-
IGI (International Gemological Institute) – Most trusted for LGDs, still uses 4Cs grading + Light Performance.
-
GIA (Gemological Institute of America) – Now issues Premium/Standard grades instead of 4Cs for LGDs.
-
HRD Antwerp, GCAL, SGL – Accepted in certain markets.
5. Compliance & Documentation Parameters
-
HS Code: 71049010 (Synthetic or reconstructed diamonds, unworked or simply sawn/roughly shaped).
-
Manufacturing Declaration: HPHT / CVD must be mentioned.
-
Stone Size Thresholds: Additional qualifiers (cut/clarity) required for stones ≥1 carat; optional for <1 carat (as per CBIC Circular 03/2025).
-
Batch Uniformity: For parcels of smaller stones (melee), consistency in size, color, and clarity is key.

Market Demand
-
Jewelry brands increasingly offering LGD collections due to sustainability & lower cost.
-
Online retail of LGDs is growing globally, especially in US and Europe.
-
Growth rate: Estimated 15–20% CAGR globally for LGDs over the next 5 years.
Factors Affecting Profitability
-
Stone Size & Quality – Larger, higher-quality LGDs fetch premium margins.
-
Certification Lab – IGI-certified stones generally sell better internationally than uncertified stones.
-
Export Destination – US and UAE buyers pay higher prices; European buyers are quality-focused.
-
Market Awareness & Branding – Lab-grown diamonds marketed as eco-friendly/ethical often command a premium.
-
Exchange Rate Fluctuations – Dollar appreciation benefits Indian exporters.
Profitability will depend on the 4Cs and Quality of the stone.
