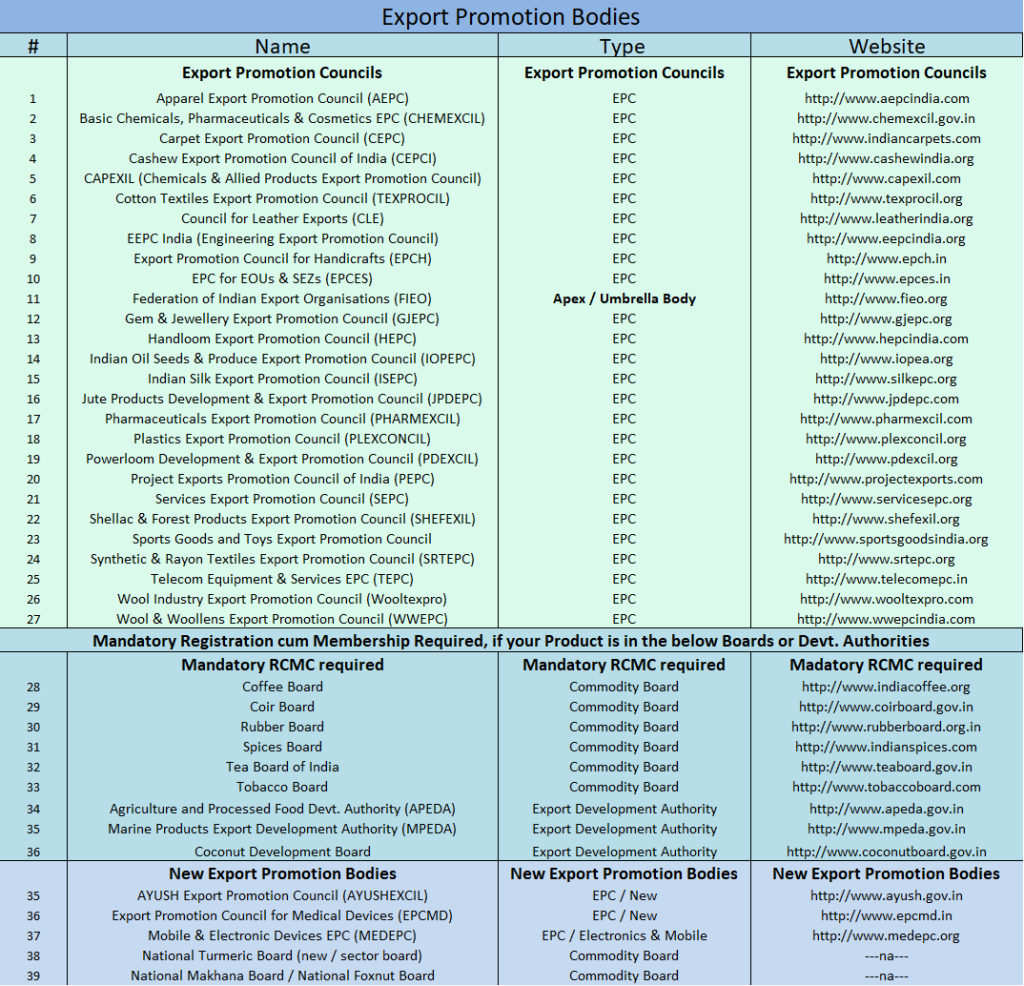
The DGFT (Directorate General of Foreign Trade) in India has created Export Promotion Bodies industry-wise.
The DGFT has deliberately created separate Export Promotion Bodies (EPBs) like
- Export Promotion Councils (EPCs),
- Commodity Boards, and
- Export Development Authorities
These bodies make the export ecosystem more specialized, efficient, and supportive.
Each Export Promotion Body organizes webinars, seminars and also local & international trade exhibitions in which the exporters can participate.
DGFT’s approach ensures that exporters are not “flying blind” in global trade. Instead of a one-size-fits-all model, specialized bodies provide:
- Sector knowledge
- International networking
- Policy and incentive guidance
- Training and quality upgrades
All of this reduces risk, increases efficiency, and improves export success.
First let us understand the purpose of these export promotion bodies:
1. Sector-Specific Expertise
- Reason: Different sectors (textiles, marine products, handicrafts, leather, chemicals) have unique challenges—standards, compliance, production methods, and market demands.
- Benefit: EPBs provide specialized guidance tailored to the sector, which a general body cannot efficiently deliver.
- Example: The Apparel Export Promotion Council advises on international quality certifications like OEKO-TEX and GOTS.
2. Promotion of Exports
- Reason: India aims to increase its global trade share.
- Benefit: EPBs organize trade fairs, buyer-seller meets, and trade missions, promoting Indian products internationally.
- Example: The Marine Products Export Development Authority (MPEDA) promotes Indian shrimp in global markets.
3. Compliance and Regulatory Support
- Reason: Exporters need to comply with DGFT, Customs, FSSAI, and international standards.
- Benefit: EPBs help exporters meet these compliance requirements, avoiding delays or penalties.
- Example: Handicraft exporters get help with geographical indication (GI) registration and quality standards.
4. Access to Government Incentives
- Reason: The Indian government provides financial schemes to support exports, but they are sector-specific.
- Benefit: EPBs help exporters claim benefits like RoSCTL, duty drawback, and market development assistance
- Example: Textile exporters receive RoSCTL benefits through their council for attending international trade fairs.
5. Skill Development and Capacity Building
- Reason: Many Indian exporters, especially SMEs, lack knowledge of international trade norms.
- Benefit: EPBs conduct training, workshops, and seminars to improve quality, packaging, logistics, and marketing.
- Example: EPCs train exporters on ISO certification, eco-labeling, and sustainable production techniques.
6. Networking and Market Intelligence
- Reason: Exporters need accurate, timely information on global demand, competition, and market trends.
- Benefit: EPBs connect exporters with foreign buyers, provide market reports, and facilitate collaborations.
- Example: Leather exporters get market intelligence from the Council for Leather Exports to enter European markets.
In general, the Commodity Boards, Development Authorities, Export Promotion Councils and FIEO are all call Export Promotion Councils (EPC).

Process to Register
- To register in the Export Promotion Body, one needs to have an Importer – Exporter Code (IEC).
- Check on the respective Council, FIEO, Commodity Board or Development Authority if you product falls in it. A product catalogue or list is given in these websites.
- Then use the “membership” or “new Members” link to go ahead.
- Registration and Membership are redirected to the DGFT website.
- After this one gets a “Registration cum Membership Certificate” – RCMC
Let us now get to know each of these Councils, Commodity Boards and Development Authorities.