Currently, the metal industry in India is booming, and it is an active exporter and importer of metals like lead, aluminum, zinc and copper.
Scrap imports has increased by 35 per cent in the first half this year to 3.87 million ton. India does not only import metal scraps. Even non-metal scraps are being imported.
India is the 2nd largest importer of metallic scrap (first being Turkey).
The present policy is to allow import of any form of metallic & non-metallic waste or scrap, as long as it doesn’t contain any hazardous material, toxic waste, radioactive contaminated waste or scrap containing radioactive material, any type of arms, ammunition, mines, shells, live or used cartridges or any other explosive material in any form.
Reasons India imports Scrap
India imports scrap mainly because of its huge demand in manufacturing and infrastructure industries but limited domestic availability. Scrap is a cost-effective raw material compared to virgin metals, reduces energy consumption, and supports India’s push for circular economy and sustainability.
Why India Imports Scrap:
- Shortage of Raw Materials in India
- India does not have sufficient reserves of high-quality metal ores (like copper, aluminium) to meet demand.
- Scrap serves as an alternative raw material.
- Cost-Effectiveness
- Using recycled scrap is cheaper than producing metals from ores.
- Reduces production costs in steel, copper, and aluminium industries.
- Energy Saving & Eco-Friendly
- Recycling scrap consumes 30–40% less energy compared to processing virgin ores.
- Helps reduce carbon emissions and aligns with India’s green manufacturing goals.
- Huge Demand in Infrastructure & Manufacturing
- India is the world’s 2nd largest steel producer and 3rd largest automobile market.
- Industries like construction, automobiles, electricals, ship-breaking, and packaging rely heavily on imported scrap.
- Circular Economy Push
- Government policies encourage recycling to reduce dependency on primary raw materials and imports of finished metals.
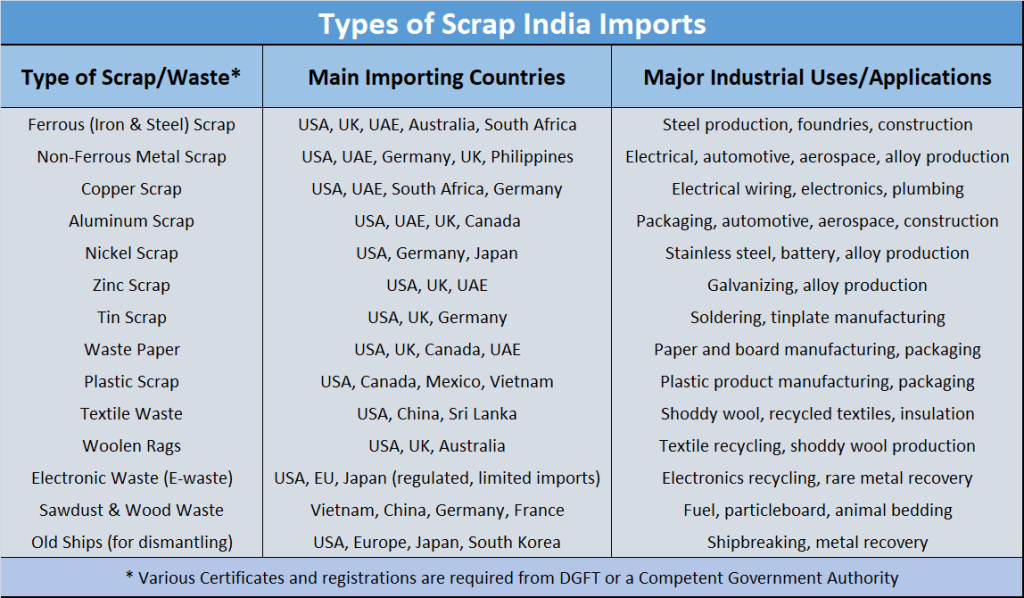
Types of Scrap and Exporting Country (India Imports)
Certificates required before Importing Scrap
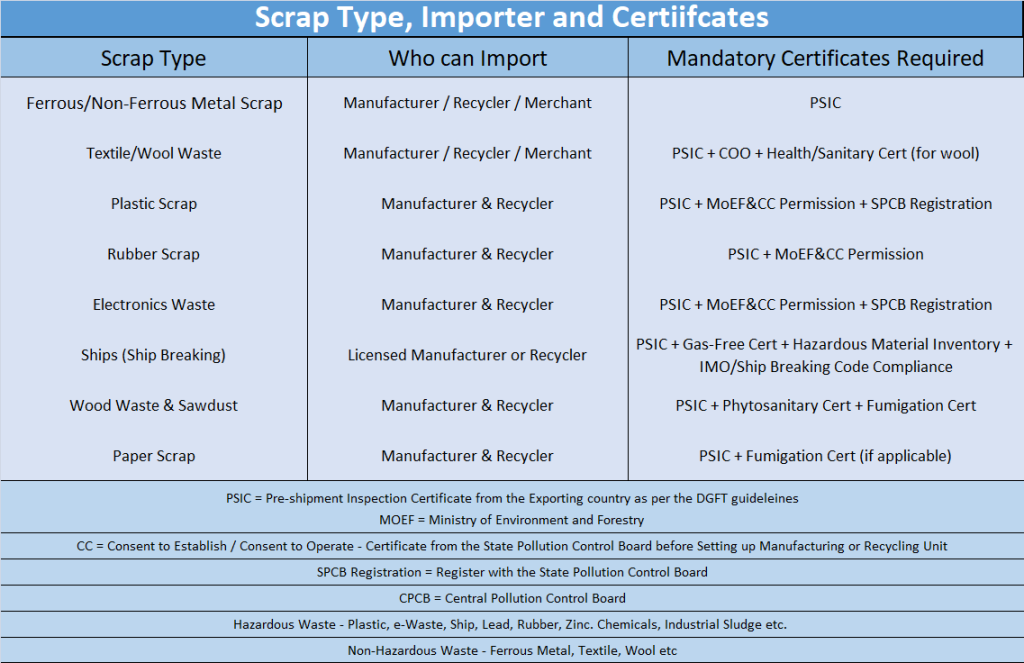
Eligibility to Import Scrap
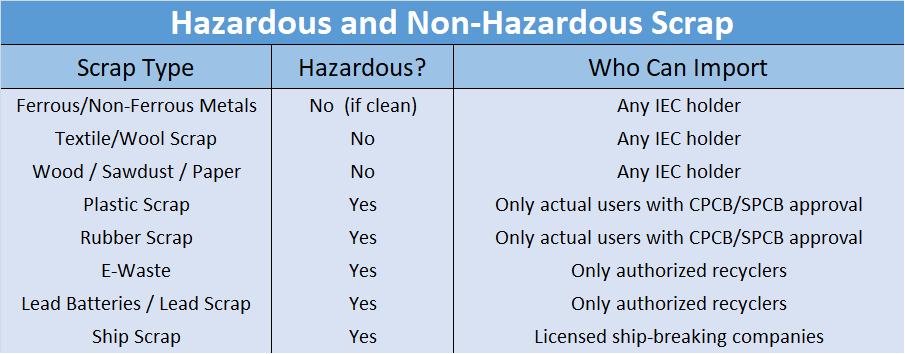
- India’s scrap import market plays a crucial role in supporting its manufacturing, recycling, and infrastructure sectors, providing a cost-effective and sustainable alternative to virgin raw materials.
- While ferrous and non-ferrous metal scraps, textiles, paper, and wood offer opportunities for a wide range of importers, hazardous scraps like plastics, rubber, e-waste, and lead-bearing materials are tightly regulated to ensure environmental and human safety.
- Compliance with PSIC certification, CPCB and SPCB approvals, and other statutory permissions is essential for smooth customs clearance and responsible recycling.
- By understanding the types of scrap, their hazards, and regulatory requirements, importers can leverage India’s growing recycling and manufacturing ecosystem while contributing to a more sustainable and circular economy.
