India Oman Trade Agreement
This is Oman’s first FTA in nearly two decades.
This agreement is India’s second comprehensive Gulf FTA, after the UAE (2022).
India’s has signed six free trade pact in the past five years, following deals with Mauritius, the UAE, Australia, the EFTA bloc and the UK.
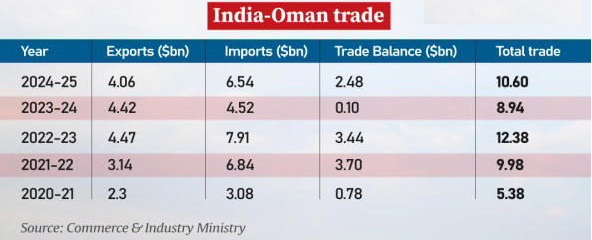
India – Oman has a bilateral trade at around $10.5 billion, dominated by energy imports. India remains trade deficit with Oman.
- India exported $4.06 billion worth of merchandise to Oman in 2024-25, which made up 0.93% of India’s total exports that year.
- It imported $6.5 billion worth of goods from Oman, comprising 0.91% of India’s total imports in 2024-25.
Key Features of CEPA
- India and Oman signed a Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreement (CEPA), in Muscat.
- Under this agreement, Oman will grant duty-free access on 98.08% of tariff lines, covering 99.38% of India’s exports to Oman.
- India will liberalise tariffs on 77.79% of its tariff lines, covering 94.81% of imports from Oman.
- Oman’s strategic location positions it as a hub for: Wider GCC markets; Eastern Europe, Central Asia, and Africa.
- Oman already has duty-free access to the US under its FTA, enhancing indirect opportunities.
Market Access and Tariff Liberalization
Products that India Exports:
Full tariff elimination for labour-intensive sectors, including:
- Gems & jewellery,
- textiles, leather, footwear
- Sports goods, plastics, furniture
- Agriculture and food products
- Engineering goods, pharmaceuticals, medical devices, automobiles
Enhanced Mobility of Professionals (Service / Job)
- Contractual Service Suppliers’ stay extended: From 90 days → 2 years, extendable by another 2 years.
- More liberal entry and stay for skilled professionals in:
- Accountancy, taxation, architecture
- Medical and allied services
Boost to the Services Sector
- Oman offers substantial commitments across key services, including:
- Computer and IT services
- Business and professional services
- Audio-visual services
- R&D, education, and health services
- CEPA allows 100% FDI by Indian companies in major services sectors in Oman via commercial presence.
Export Opportunities for India
Indian exports to Oman have doubled over the past five years.
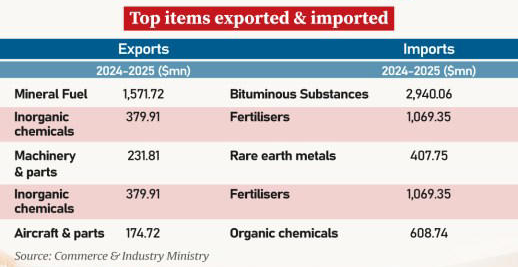
Key exports include machinery and parts, aircraft, rice, iron and steel articles, beauty and personal care products, ceramics, and petroleum products such as naphtha and petrol.
Zero-duty access on 98% of Oman’s tariff lines under the CEPA is expected to boost competitiveness, especially for industrial goods, though sustained growth will depend on quality upgrades and product differentiation.
With more than 6,000 India–Oman joint ventures and Indian investments exceeding $7.5 billion, particularly in Oman’s Sohar and Salalah free zones, the CEPA is as much about geopolitics and regional presence as it is about tariffs. For India, it represents another step in cementing its economic footprint in the Middle East.
CEPA between India and Oman is signed to be implemented after ratification by both the country’s parliaments. By the end of 2st Quarter of 2026 this India Oman CEPA is likely to be implemented.
